- Data Migration
- Improving Data Quality: day-to-day actions
- Using your data in D365FO today: Reporting
- Using your data in D365FO Tomorrow: Copilot
During the test sessions and then in production, it is common to hear users complain about the quality and reliability of data, generating frustration and errors in systems ranging from incorrect data to the impossibility of running flows. Although these data reflect individual impressions, they indicate that the quality of the data is often perceived as poor.
Several questions may arise why this feeling and mistrust towards data. Can the facts justify it or is it just a feeling of users? And what is data quality exactly? Sometimes it is more like a concept than something on which we can work. And why is data quality so important when working in D365FO?
In this article, I will share some concepts about the importance of data quality.
Let us take an example of the current life: Imagine you order a pizza. You order the pizza and indicate which pizza you want. They note your address and, depending on the time agreed upon, the delivery person brings you the pizza exactly as you ordered it. You pay the delivery guy and enjoy your meal. It is simple, everything goes well.
Now what happens if you place an order, but they save an incorrect address. Due to this error, the delivery person arrives at the wrong address where people are not aware of the pizza order. The delivery person must then contact the pizzeria to clarify the problem and ask for advice. Luckily, the pizzeria has correctly noted your phone number and calls you. With your help, they correct the address. It sends the exact address to the delivery person. The delivery man finally arrives at your location, but the pizza has become cold in the meantime, and you are unsatisfied with the delivery and your pizza.
This is a simple example, but it is perfectly representative of what we call data quality. An error in the data (by entering an incorrect address) caused the following additional actions on the ordered pizza:
- The delivery person is wasting time by going to the wrong address.
- The delivery person must make an additional phone call to the pizzeria to explain the problem and ask for help.
- The people at the pizzeria should make an additional phone call to the customer for your help in noting the correct address.
- The delivery person needs extra time to move from the wrong address to the right address.
- As a customer, you are not very satisfied with the delivery time and with the pizza that has become a little cold.
All these extra operations created from user dissatisfaction but also additional costs.
Now back to the data quality topic for D365FO with examples:
- Some organizations had incorrect payment terms in the customer or supplier master data in D365FO. Based on this, the transaction information is not correct. The consequences: discussions with customers or suppliers about payments, collection letters sent unnecessarily, discounts not deducted even when authorized. Result: more money spent than needed, less customer satisfaction and a lot of extra work and frustration for the organization’s employees.
- Other organizations with incorrect stock quantities in D365FO. The consequences: employees with their own Excel lists because they do not trust the figures of D365FO, customer orders that cannot be delivered because the warehouse does not have the goods, Missing stocks due to a misplaced location mentioned. Result: a lower in customer satisfaction, extra work, and lots of frustration.
- Incorrect financial figures from D365FO. Consequences: decisions made based on erroneous information. Result: additional time needed to clarify differences, additional time to reconsider decisions made, including consequences already made.
So, it is important to define what data quality is and why is it important to manage it?
To ensure that processes can be run efficiently in D365FO, process data must be of excellent quality. And then it is important to determine which elements are part of the construction of good data quality:
- Reliable: Data must be based on reliable sources.
- Correct: data must be correct and free of errors.
- Consistent: data must be consistent across the overall business chain and applications used by the business.
- Completeness: all necessary data must be available.
- Timeliness: data must be up to date and available on time.
- Relevant: data must be relevant in the context of business processes and associated decision making.
- Unambiguous: all employees have the same interpretation of data, regardless of their role and experience in the organization
Data is gold. But the gold value of your data depends on the quality of your data.
Data Migration
Strategy
For this purpose, first it is important to define a data migration strategy: is the name that will be given to all the processes aimed at extracting, conditioning, verifying, and injecting the data present in the old computer system to the new one.
It is realized in eight successive steps, which are valid for each subsystem to be migrated:
- Step 1: Systems Identification (“Evaluation”). Systems whose data are to be retrieved and integrated into D365FO are identified.
- Step 2: Identification and extraction of data. The data are recovered in the system to be migrated, by any technical means available (extraction, report, copy of files, database export, etc.).
- Step 3: Build data test plans. This phase is at the sole discretion of the business line, which is responsible for building test plans to verify, in the target system (D365FO), that all the data have been correctly and exhaustively taken over.
- Step 4: Identification and selection of the data to be recovered (“Data Cleaning”). Based on the work of phase 3, the business scans the data made available in phase 2 and is responsible for selecting the extracted data that must be transferred, correcting them, and transcoding them.
- Step 5: Identification of suitable D365FO tools and construction of the data mapping strategy. The extracted data selected by the business line is reformatted to be put in an understandable format by the selected data recovery tool. It is at this stage that mappings are made to give all the correspondence between the original data and the data to be injected into the system.
- Step 6: Data Loading. The formatted data is injected into D365FO.
- Step 7: Data Verify. The data is now present in the final information system. They are then reviewed and qualified by the business users who declare them suitable to serve, based on the work conducted in phase 3.
- Step 8: Data release and transition support. The data is injected into the final production ERP environments for daily use, and any subsequent deltas between the target and the real ones are sent on a case-by-case basis by dedicated working groups where business lines and technical stakeholder’s coordinate.

Golden Rules
To make the migration process easier, a migration strategy is supposed to:
- Work only on necessary data.
- Avoid outstanding complex transactions.
- Avoid unnecessary history.
- Avoid bottlenecks in the migration.
In one word: simplify. This means:
- Work on necessary data only: cleansing & selection are mandatory.
- Remove old undelivered Sales Orders
- Remove old not received Purchase Orders
- Remove old bad debts in accounting.
- Close old inactive customers & suppliers
- Remove all inactive and useless items.
Do not migrate unnecessary complex transactions: simplifying is mandatory.
- No Sales Orders at picking stage: Sales Orders on picking must be delivered and invoiced before migration.
- No Sales Orders delivered but not invoiced: Sales Orders delivered must be invoiced before migration.
- No Purchases Orders received not paid limit volume.
- No Purchases Orders paid, but not received.
Do not migrate unnecessary history: when required consider migration in BI data warehouse.
- No history in accounting if possible (only unpaid transactions, and balances)
- No cost history unless it is business critical.
Avoid bottlenecks in the migration in the go live session: when possible do not migrate too many data in too little time.
- Migrate most history in advance.
- Migrate most master data in advance (customers, suppliers, products, prices,): progressive cleansing, enrichment, and validation.
- On Go Live migrate only the latest modifications or creations: only outstanding transactions, open accounting transactions, stocks & values during the go-live weekend.
To achieve this data migration, it is also important to rely on deliverable and tools:
- The Data Migration Requirement (Word Document): Framework in term of methodology
- Standard Template (Excel Files): Data Migration Contract for Exchanging Data
- Data Migration Tools: Accelerate & industrialize Data Migration
- Setup in GCF (ex: Chart of Accounts, location for Warehouse)
- Theoretical Planning for Dry Runs (to be adjust with capacity of realize Templates and specific developments)
Dry Runs
Finally, to obtain high data quality, it is important to perform multiple Runs whose main objectives are:
- Verify that the technical tools are consistent and working Properly.
- Make sure that we can extract / clean up data from Systems.
- Be able to make a proof test and low in D365FO with those data.
- May have distinct experience if we make transaction based on data directly creating and dynamics versus If we make transaction with data coming from the former system: control that there is no issue on that.
First Dry Run:
- First Data Migration Run once data Model is stabilized: Need To be Synchronized with Development
- Go through process related to the Master Data (Before to Master Data Combo in Planning): Integration Testing
- Master Data Combo: Data Migration + Setup + development Ready -> Have a Session with Business team to present Process.
Second Dry Run:
- Go through the Main process with transactional data migrated (not the full volume of data): Integration Testing
- End to End flow for purchasing, sales, manufacturing, finance.
- Realize fine Tuning on program to do better Migration and process.
- Highlight some issue on data quality.
- Update Cut Over Plan: It is a technical and Business tasks for Data Migration. Also, all the Preparation Work related to the Cut Over (Example Inventory in Warehouse to get it through the full situation, the labelling : relabel the location need to be done in advance, implementation of printer or terminal and setup).Define the planning of tasks than can be perform before to provide visibility
- Time tasks realization (Tasks with online old system is working and some tasks will be done during offline. Ex Finished Old System on Friday and start with the new one on Monday: means that offline task they must be performed only in 48 hours: finance, inventory, Reconnexion of Interfaces, printers, users)
Third Dry Run:
- Go through the Advanced process (The full scope templates, all the types of data and additional specific fields for data structure): Integration Testing
- End to End flow for MRP, Forecast process, End of year closing.
- Same Tasks: Tuning, Treat issues for quality data, Update Cut Over Plan and Time Tasks
X Dry Run:
- Before need to pronounce OK for data migration programs, developments, interfaces, reports, and setup testing.
- Environment Ready: Architecture readiness, connected to external tools (interfaces); terminals, printers….
- Finalize Tuning, Treat issues for quality data, Update Cut Over Plan and Time Tasks
Improving Data Quality: day-to-day actions
Many workspaces are available in D365FO, to continuously improve the data and avoid its deterioration. Let us review these tools.
Data Maintenance
Data maintenance enables simple scheduling processes that you can run to find or correct data inconsistencies in your environment.
Incorrect data can adversely affect your day-to-day, monthly, and yearly operations. Inconsistencies and errors that come from incorrect data has the potential to halt major events like year-end activities and can even halt your daily revenue streams and affect your organization’s decision-making capabilities.
The Data Maintenance Portal is a tool that lets system administrators schedule and run various actions that will have a direct effect on the data or the system.
Some actions can be scheduled to continuously look for opportunities to fix issues, and others can be run on demand to enact some change on the system. Currently there are three basic types of actions: direct, scanning, and fixing.
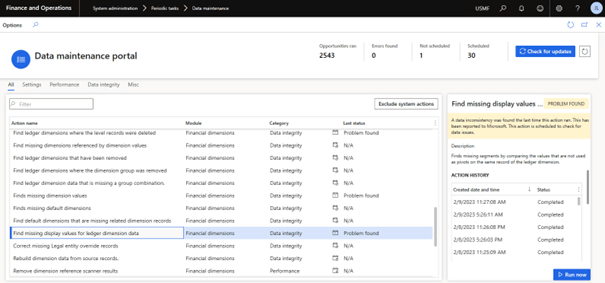
To access the Data Maintenance Portal, administrators you can go to System administration > Periodic tasks > Data maintenance.
On this page, administrators can see the list of actions that are available, and the latest status of each action. Essential information about the action can be found in the right panel.
If the action can be scheduled, there will be a button labeled Schedule available at the bottom of the page. All actions can be run on demand, prior to being run by the automated schedule, by selecting the Run now button. System actions, defined by Microsoft, cannot be disabled, or enabled.
The recurrence of data maintenance processes is handled by the process automation framework as background processes, for this reason is strongly necessary that you validate that your environment have the «Process automation polling system job» running. You can initialize this one on System administration > Setup > Initialize background process.
Exist three type of actions that you can do:
- Direct actions can be run on-demand only and can run tasks directly.
- Scanning actions will search your data, a few times a day, looking for problems in the data. The problems found will be reported to Microsoft.
- Fixing actions runs on the same cadence as a scanning action, but when an opportunity is found, it will schedule a fix to the data. Fixing actions are meant to be data idempotent and may not fix all the data on the first run.
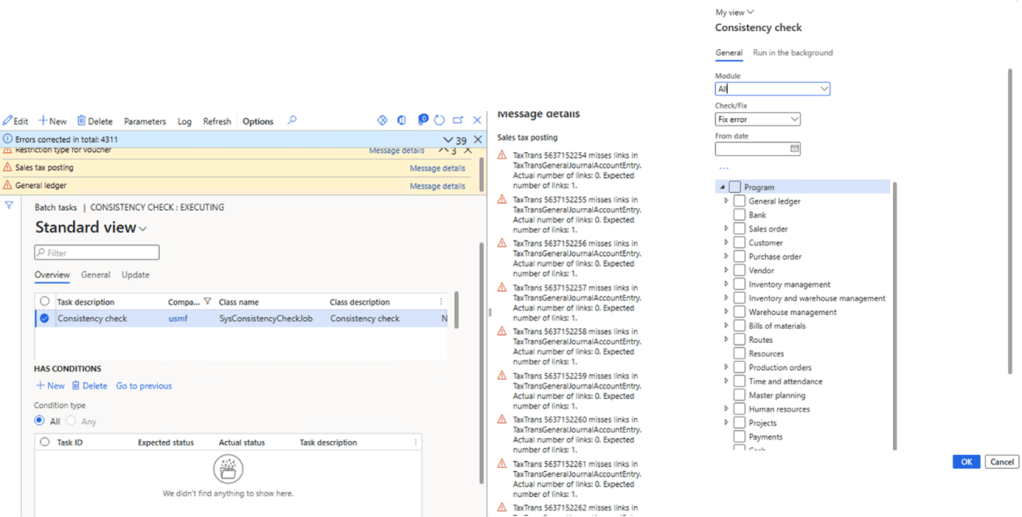
Consistency Check
If you are a long time AX user, you may be familiar with the consistency check process. This functionality has been available since AX 2009, in AX 2012 and it is still available in Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations.
This tool is used as way for a user to check/fix the system for orphan records. Orphan records are created because data was deleted, but the transaction still exists in a related table. These records can cause performance issues and, in some cases, prevent a user from completing their business processes.
To check the data consistency run the batch job Consistency check: In System administration > periodic tasks > Database > consistency check.
Optimization Advisor
Incorrect configuration and setup of a module can adversely affect the availability of application features, system performance, and the smooth operation of business processes. The quality of business data also affects system performance, and an organization’s decision-making capabilities, productivity, and so on.
The Optimization advisor workspace is a tool that lets power users, business analysts, functional consultants, and IT support functions identify issues in module configuration and business data. Optimization advisor suggests best practices for module configuration and identifies business data that is obsolete or incorrect.
Optimization advisor periodically runs a set of best practice rules. A default set of rules is available; however, users can also create rules that are specific to their customizations When a violation of a rule is detected, an optimization opportunity is generated and appears in the Optimization advisor workspace. A user can take appropriate corrective action directly from the Optimization advisor workspace.
When you act on some optimization opportunities, the system calculates the impact of the opportunity in terms of the reduction in the runtime of business processes. Unfortunately, this feature is not available for all optimization opportunities.

To view the complete list of Optimization advisor rules and to see how often the rules are evaluated, go to System administration > Periodic tasks > Maintain diagnostics validation rule. Only rules that have a status of Active are evaluated. The evaluation frequency can be set to Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Unscheduled.

Data Cleaning
In Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, cleanup routines are available in various modules.
These cleanup routines should be run only after the business has done detailed analysis and confirmed that the data is no longer required.
Always evaluate each cleanup routine in a test environment before you run it in a production environment.
Using your data in D365FO today: Reporting
In today’s data-driven business world, effective decision making relies on clear visibility into organizational performance. D365FO offers a comprehensive suite of reporting tools designed to enable users from all technical backgrounds to transform raw data into actionable information.
- Financial reporting: Finance professionals can leverage pre-configured reports such as balance sheets and cash flow tables, providing a fundamental understanding of the financial health of the organization. D365FO also provides users with a report design tool. This feature allows for customized reports, allowing users to tailor reports to specific department needs or create consolidated reports for enterprise-wide financial analysis.
- Electronic reporting: D365FO’s electronic reporting functionality goes beyond traditional report generation. It facilitates transparent data exchange, including tasks such as:
- Automated Bank Statement Import: Effortlessly integrate banking data into the financial system, ensuring data accuracy and streamlining reconciliation processes.Simplified data export: Comply with external reporting requirements or facilitate easy data sharing through efficient data export capabilities.
- Integration of predefined formats: Use pre-configured templates for reporting scenarios.
- Advanced reporting: D365FO integrates seamlessly with Power BI, a powerful business intelligence tool. This integration unlocks the potential for advanced data analysis and visually appealing dashboards that communicate information effectively. Uses Power BI, a well-known reporting and dashboard tool, to enable users to create relevant reports and interactive dashboards. Regardless of your experience with Power BI, the built-in experience enhances data visualization capabilities and integrates with other Fabric features.
D365FO Data & Fabric
Since the end of 2023, it is now possible to link to your D365FO data, directly from Microsoft Fabric. No need to build ETL pipelines or manage data refresh, your data is readily available. You can work with your data in Microsoft fabric to create reports or to work with T-SQL.
Microsoft Dataverse direct link with Microsoft Fabric enables organizations to extend their Power Apps and Dynamics 365 enterprise applications, and business processes into Fabric. The Link to Fabric feature built into Power Apps makes all your Dynamics 365 and Power Apps data available in Microsoft One Lake, the built-in data lake for Fabric.
- No need to export data, build ETL pipelines, or use third-party integration tools.
- With shortcuts from Dataverse directly into One Lake, your data stays in Dataverse while authorized users get to work with data in Fabric.
- Link data from all Dynamics 365 apps, including Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps.
- Build Power Apps and automations to drive action from insights in One Lake.
Microsoft Fabric is a complete platform that streamlines data analytics workflows. It provides organizations with a consolidated platform to effectively manage and analyze data. This end-to-end unified solution serves as a “one stop shop” for data tasks, from data ingestion and transformation to visualization using Power BI.
Its consistent platform allows for effortless transitions between key features such as:
- Data Engineering
- Warehousing
- Data science
- Real-time Analytics
- Data factory
- Power BI.
Fabric integration with a specialized “Data Lake” further enhances its capabilities by storing data in versatile formats such as Delta, Parquet, CSV, and JSON.
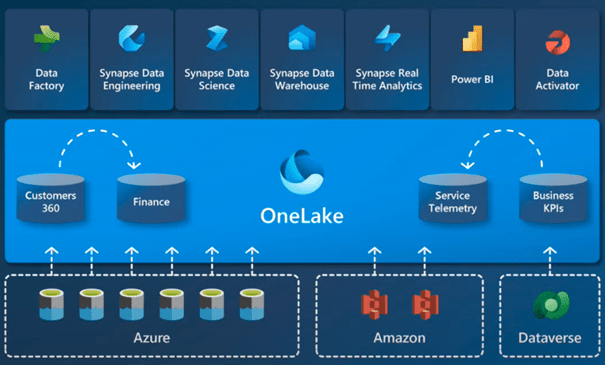
Microsoft’s strategy with Microsoft Fabric is to centralize data in what they call a “One Lake.” This system allows you to create several “Lake Houses” and workspaces within the One Lake.
Data can be imported into a lake from sources such as Dynamics 365 or Dataverse or linked via shortcuts to external file systems such as Azure ADL, S3 or Dataverse. These shortcuts function as pointers to data stored elsewhere, eliminating the need for redundant copies. The advantage of this configuration is that it eliminates the need for separate ETL processes for different tasks such as data science or reporting.
All processing is done in Fabric, whether for machine learning, reporting in Power BI or other analysis tasks, using tools such as Data Factory for ETL and Power BI for visualization. Data is ingested or routed to One Lake, allowing users to process and use it in various analysis and reporting functions.
Enable Microsoft Fabric with D365FO
To effectively integrate D365FO with Microsoft Fabric, you need to use specific methods in the Power Apps Make portal to route your data.
There are two approaches to completing this process:
Using PowerApps Maker Portal: Link to Microsoft Fabric
- In the Power Apps Maker portal, locate and pin the option “Azure Synapse Link” in the left menu if it is not already visible.
- Click “Azure Synapse Link” and select the link that you previously set up as a Synapse link to Dataverse.
- Access “Link to Microsoft Fabric” by clicking on the ellipsis (…) next to the link.
- In the pop-up window, use the drop-down list to select the workspace you want to link to.
- This method allows users to select, manage and add tables from Dataverse and D365 Finance and Operations.
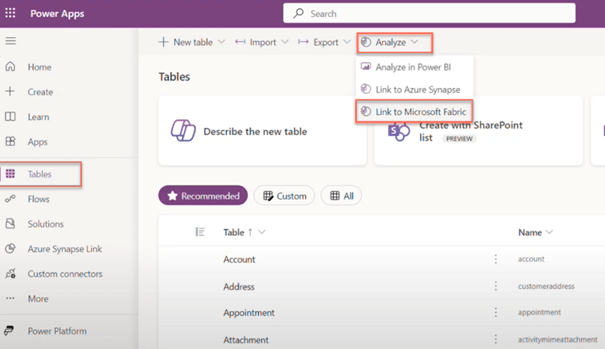
Using Azure Synapse Link within Power Apps Maker Portal
- In the Power Apps Maker portal, locate and pin the option “Azure Synapse Link” in the left menu if it is not already visible.
- Click on “Azure Synapse Link” and select the Microsoft Fabric (One Lake) link associated with the desired workspace.
- Access “Manage tables” by clicking on the ellipses (…) next to the One Lake link.
- This method allows users to select, manage and add tables from Dataverse and D365 Finance and Operations.
To use this method, you must have previously configured an Azure Synapse link for Dataverse to enable data storage and analytics integration.

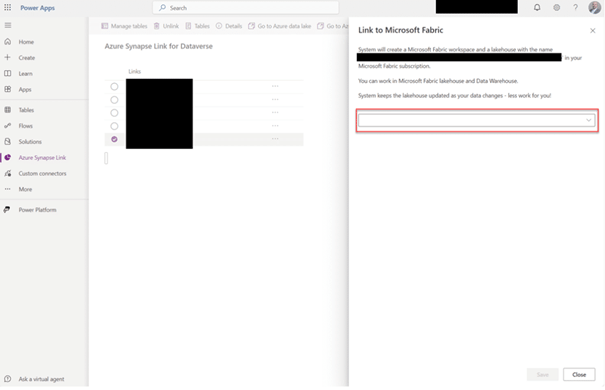
Both approaches offer flexibility in integrating D365FO with Microsoft Fabric.
The first method links directly from the Power Apps Maker portal, allowing users to choose specific tables to embed, but downloads all tables from Dataverse. The second method leverages the Azure Synapse link configuration, providing more customized control over table selection in the fabric environment.
After you have configured the integration, you can access the designated workspace in Microsoft Fabric to manage and use interlocked data effectively.
Using your data in D365FO Tomorrow: Copilot
Regarding the data in D365FO, Microsoft introduced the Copilot context aware summaries. For example, you can now find the fast tab “Summary by Copilot” on the vendor master data card:

These Copilot contextual summaries are available on different forms. For example, on forms related to the supplier, customer, purchase order.
If you do not see the summaries already, in the Feature management list in D365FO you can filter on the word ‘summary’. You will find the list of available context aware summaries:

For example, also the feature related to product information:
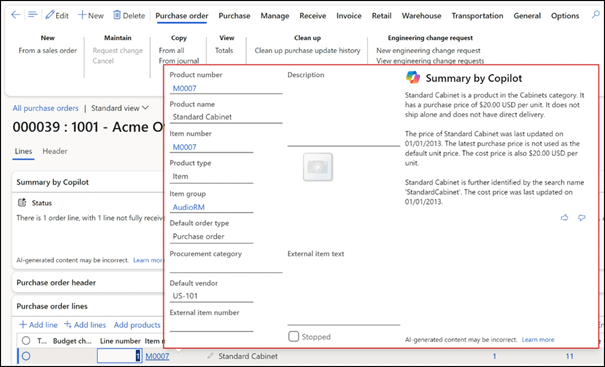
Context summaries provide a quick overview of the most essential information related to the form you have opened. Summaries are customized for the user who opens the form based on the context of the user.
Users will be informed quickly of the most valuable information, allowing them to act more quickly when needed:

Users are informed of situations to follow:
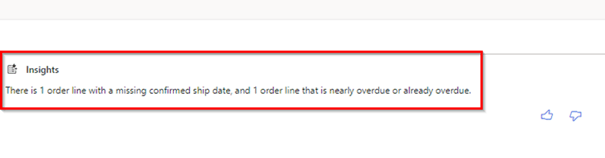
Users will find relevant information faster based on their context and role in the business. With this information, existing data in D365FO can be verified and improved consistently as needed by resolving any errors or inconsistencies. They can help enrich and refine data and support decisions and actions.
These new contextual summaries of D365FO will only be usable if the data quality is up to date. This will only happen when users learn to focus on data and understand the effect of data quality on their role in the business process. Organizations should also ensure that responsibilities for data entry or update are defined. You need to focus on awareness of data quality and user skills. Investing time in this area will improve benefits:
- In D365FO, processes are integrated. Good data quality streamlines the process chain and ensures that employees can execute the process with the least amount of effort. This reduces the need for corrections and retouches that always cost a lot of time and frustration.
- Reliable and accurate data will be the basis for good decision making.
- Correct and complete data helps to serve the customer well, resulting in greater customer satisfaction.
- In many sectors or regions, regulations are in place that require data to be reported and with all the sustainability regulations this will only increase. Good data quality meets these requirements.
Leave a comment