- Configure a hierarchy of processes, roles, and privileges
- Security tasks under the process hierarchy
- Security entry points under the process hierarchy
- Roles violating segregation of duties
Let us take a closer look at the useful features added as part of the User Security Governance module. One of the main forms is a page where you can manage maintain a security process hierarchy and roles with their contents. This is an additional way to create security roles next to the security configuration form or using Visual Studio. The purpose is to make role creation faster and easier. In addition, version control is supported, which is a requirement in many industries.
With the Security category created previously, you can create a hierarchy by clicking + New process. Reselect the first node if you want to add more elements to the root. Each level of the hierarchy supports the creation of a role. I would not recommend creating roles at the end-to-end scenario level, but you can create another level for each role. Depending on your preferences or needs, you can first add another level before the actual security role level.
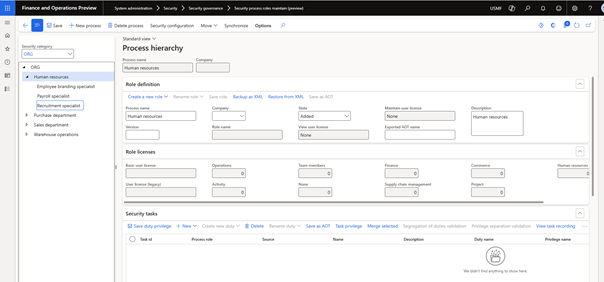
Once the initial hierarchy is complete, you can export a backup for later restore or another environment. When you want to create a role, you must click on Create a new role in the action bar of the Role definition section. This will launch a placeholder for a newly configured security role.
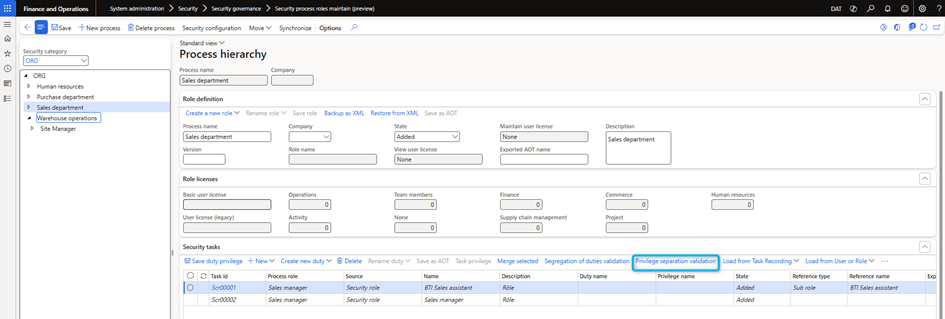
You can use the task recorder to record all the actions that must be part of the new security role. The task recorder will contain details about open pages and actions performed. You can load the saved task record using the action called Load from task recording which is “hidden” behind the … (more) as shown in the screenshot below.


It is possible to enable or disable the options Include table permissions and Include control permissions which allows to limit the list with only saved menu items. Disabled options will add table permissions for all tables used on saved forms. The same applies to form controls.
The import has some logic to determine whether, during the save, only one page was opened or if several actions were performed, such as adding or deleting records. It will create a list of required entry points, including the discovery access requirement. Thus, if you need full access to particular menu items, make sure to add and delete a record while saving the task. You can always update permissions when the list is displayed on the grid.
The next step is to check existing duties and privileges.
The idea of security architecture is to have a role consisting of one or more duties and for each duty one or more privileges that can be reused as building blocks.
Configure a hierarchy of processes, roles, and privileges
A process hierarchy allows you to organize and manage the business processes in your company. After you have defined the process hierarchy for your company, you can assign various tasks and define roles, entry points and privileges based on business needs.
This feature allows you to configure your company’s security configuration based on position-based roles and duties/privileges. New roles can be created based on the organization’s hierarchy and existing positions. Therefore, the feature helps you create optimal roles that consider user interface (UI) efficiency, license levels and data security.
The functionality extracts business processes from positions and converts them into security roles. Therefore, roles are easy to understand and define. The objective is to implement roles that represent the specific set of tasks and privileges required to perform single work in D365 Finance.
The benefits of this feature are the optimization of license costs and reduction of data fraud risk.
Configure a process hierarchy
The first and most crucial step in the configuration process for a specific security configuration is to define a process hierarchy that closely represents your company’s functional hierarchy. Although the process hierarchy you define can be changed later, the change requires a lot of work.
To configure a process hierarchy, follow these steps.
- Go to System Administration > Security > Security Governance> Security process role maintain.
- In the Security Category field, choose a category and then select the level of the tree you want to use in that category.
- In the Actions pane, select New Process.
- In the Process Name field, enter a unique name for the process.
- Specify other details such as a description and version information.
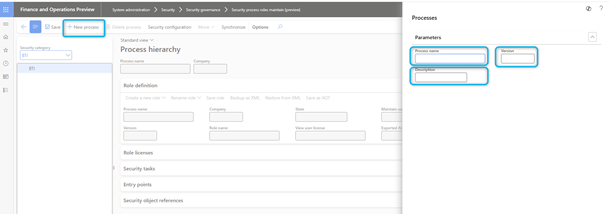
Create tasks for the process
A task represents the smallest end-to-end functional steps that a role performs. There are two ways to define tasks for a process level:
- Create a task and manually define the entry points.
- Use an existing task record that represents the functional behavior of any desired role.
To create a rule, do the following:
- Go to System Administration > Security > Security Governance Security process role maintain.
- Under Security Tasks, select New.
- In the Name field, enter a value.
- In the Description field, enter a value.
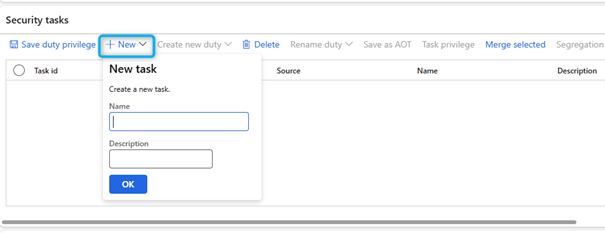
- Select Create new duty to create a duty for the task.
- Enter a value in the duty Name field.
- In the Description field, enter a value.
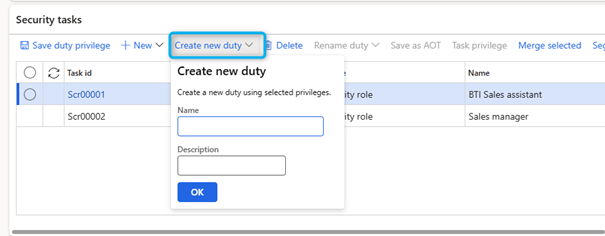
- Once you have created the duty, a privilege is automatically created for it. This privilege is named after the duty for which it was created.
Assign an entry point
Menu items, web content items and service operations are collectively referred to as entry points. Entry points define the starting points of a task or duty in the execution of a function. Multiple entry points can be assigned to each task.
To assign a point of entry to a task, do the following:
- Go to System Administration > Security > Security Governance > Security process role maintain.
- Go to Security Tasks and select the task to assign the entry point to.
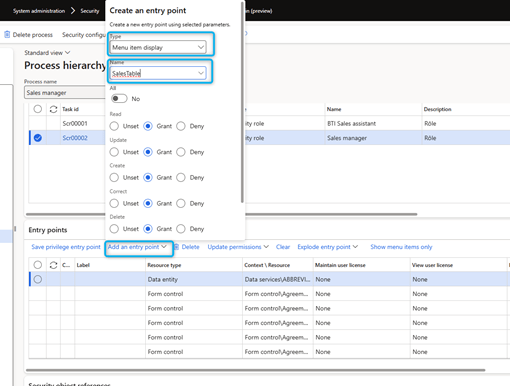
- Go to the Entry Points and select Add an Entry Point.
- In the Type field, select one of the menu item types.
- In the Name field, select one or more identifiers. Each identifier represents a unique menu item, web content item or service operation.
- Under each permission level, set the permissions to read, update, create, correct, delete, and invoke.
- Repeat steps 3 to 6 to add entry points to the task.
- When you are finished, select Save Privilege entry point.
Create a role
A role is the set of duties and privileges required to perform a specific task. Roles are created by combining multiple duties and privileges. Once you have defined the process hierarchy, tasks and entry points, you can create new roles.
To create a role, follow these steps:
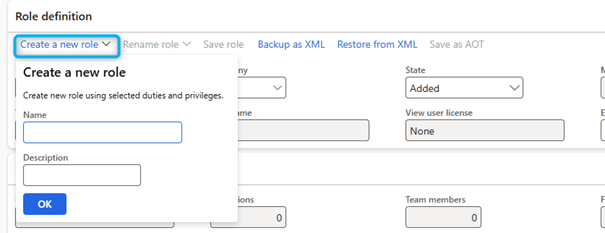
- Select a process hierarchy level, then in the Process Definition FastTab select Create a new Role.
- Enter a value in the Role Name field.
- In the Description field, enter a value.
- Save the role.
Merge option under security tasks
The Merge operation merges the entry points from the selected tasks into the destination task and is useful when consolidation of tasks is recommended for a given role.
To merge tasks, follow these steps:
- Go to System administration > Security > Security governance > Security process role maintain.
- Go to Security tasks, and select more than one tasks to merge together.
- Currently, the task selected last is designated as destination and all other tasks selected before are merged into the destination.
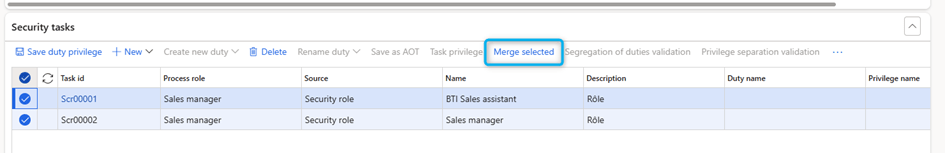
Two merge options are available:
- merge entry points and delete underlying duties and privileges from the selected tasks.
- merge entry points from selected tasks into destination and preserve the underlying duties and privileges.
To use the merge operation, select more than one task.
Synchronize security governance process hierarchy with core security configuration
Synchronize function syncs any changes done directly into security duties and privileges on the Core security configuration page.
When duties, privileges, and roles are created from Security governance and published to core security configuration, users can edited them in Security configuration by either adding or removing entry points. By doing this, the security object is different between two pages.
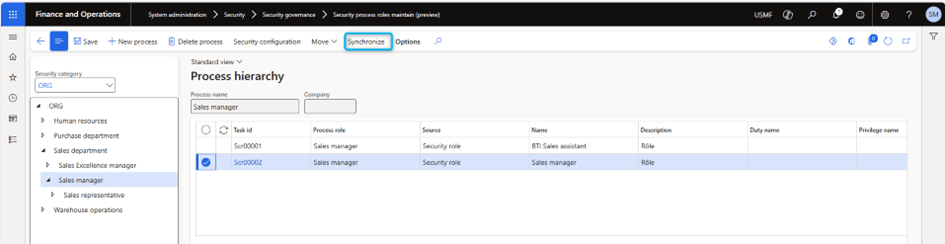
To restore changes from security configuration into security governance, use the Synchronize feature by selecting a process hierarchy level.
- Go to System administration > Security > Security governance > Security process role maintain.
- On the header, select Synchronize to use the feature.
Security tasks under the process hierarchy
Security tasks under the process hierarchy are the key processes that a given role performs in D365 Finance to perform its specific tasks. This feature allows system administrators to convert these processes into individual tasks and into multiple features supported by those tasks.
Segregation of duties
Segregation of duties prevents overlapping duties with overlapping privileges and roles with overlapping responsibilities. The task allocation can be activated on the Parameters page. After creating a task and assigning entry points, you can validate the percentage of overlapping responsibilities. You can set up task segregation of duties rules to prevent users from recording conflicting duties.
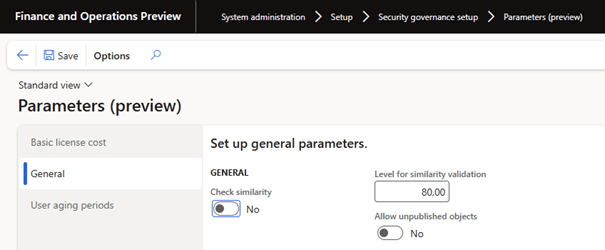
Validation of privilege separation
Privilege separation validation is more focused on role privileges that are assigned to roles. After creating a task and assigning entry points, you can validate the percentage of overlapping privileges.
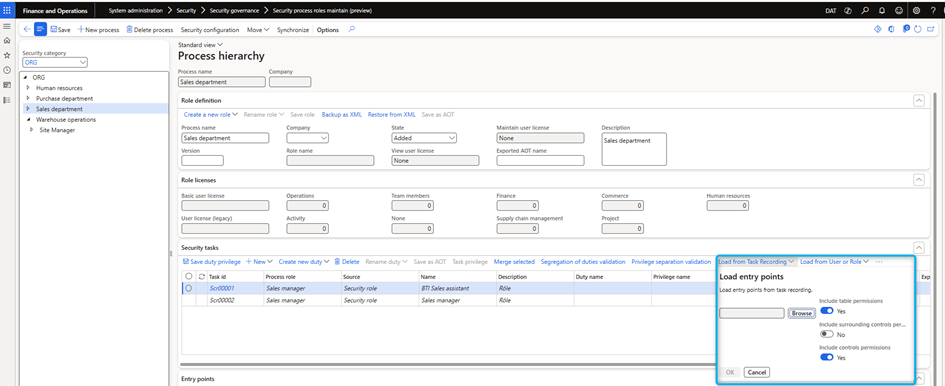
Load from task recordings
Create tasks from existing tasks recordings that are generated by capturing user interface (UI) interactions in the task recorder tool. Users can record key business actions and share records with system administrators. System administrators can then convert the records into security tasks in the security configuration. This approach provides an effective way to create tasks.
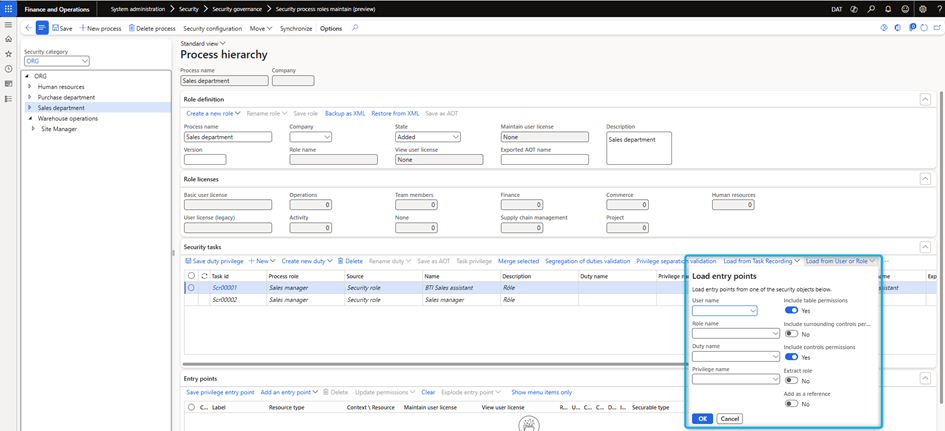
Load from a user or role
Convert existing user account or role entry points into security tasks. After selecting an existing user account or role, the entry points are extracted and converted to tasks. System administrators may have a starting point to design a new security role based on existing users or roles. They can add, modify, or remove additional entry points from the extracted entry points and define a new role with new duties and privileges. System administrators can quickly create new roles that are inspired by existing roles within the company but do not overlap completely.
Load from an existing task
Use existing tasks as a starting point to create new tasks.
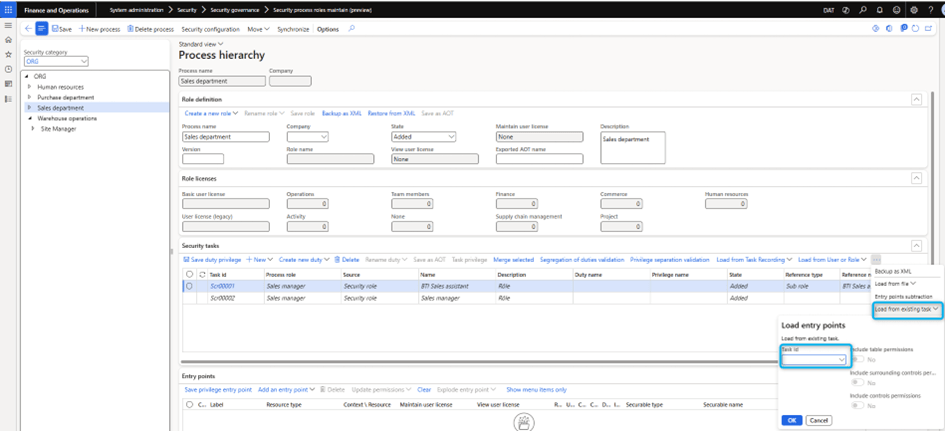
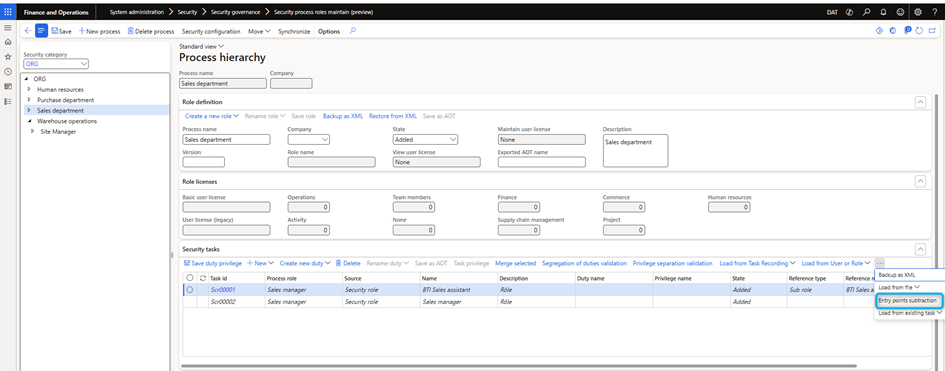
Subtraction of entry points
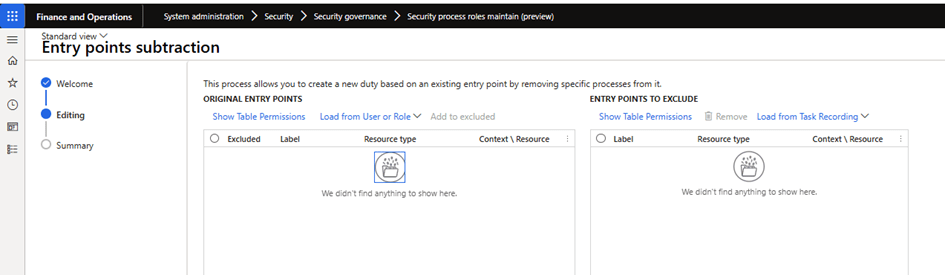
Create a task based on an existing entry point by removing specific processes from it. Select Entry Point Subtraction and then select an existing user account, role, privilege, or duties to view the entry points. You can remove all entry points that you do not want to create in the new tasks.
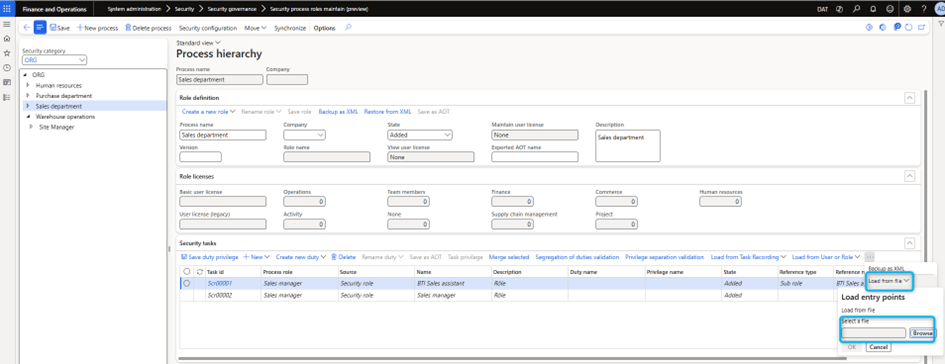
Load from file
Use an existing XML backup file to create new tasks. When you copy tasks from one company to another, export the source company’s tasks first in XML format. Then import them into the destination company.
Security entry points under the process hierarchy
The security entry points under the process hierarchy are essential to define and design the level of access and privileges for a given role. Some key functions related to the entry points that are supported in user security governance include:
- Explode the entry point.
- Update authorizations
Explode the entry point
System administrators can extend the permissions of a given role to include all other entry points related to the menu item. The menu item associated with the entry point is retrieved using its name and type. The system then extracts all other entry points associated with this menu option. If the menu option exists, access rights and labels are set for the entry point. If the record type is a menu item, other properties are defined, such as user licenses and manual permissions.
This function adds all the neighboring entry points from the selected entry point. I recommend using it with workspaces.

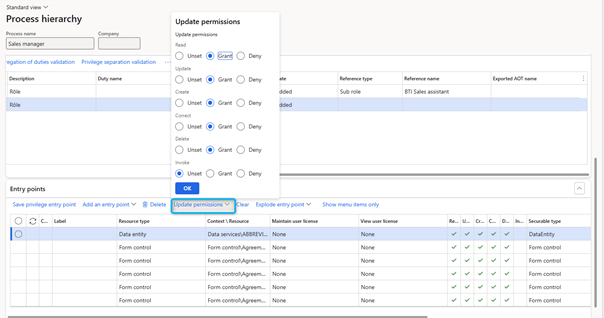
Update permissions
System administrators can update permissions for a given role by changing the permission levels for each entry point.
For each entry point, the Deselect, Grant, or Deny permissions can be reconfigured to the following levels:
- Read
- Create
- Update
- Correct
- Invoke
- Delete
Roles violating segregation of duties
Until now, in D365 Finance, you could set up segregation of duties rules that would then check for violations when security roles were assigned to a user. In user security governance additions, there is an option to check for a violation in separate security roles before assigning them to users. This will ensure a smoother process for creating compliant roles and avoid mitigations when a user is assigned to such a role. You can check for possible violations when creating the security role. There is also a form where you can check all roles, including existing security roles.
The Roles violating segregation of duties view displays all the roles that violate the segregation of duties rules. It also indicates the number of such violations existing for each role.
View violations for a selected role
To view violations of segregation of duties rules, follow these steps:
- Enable the Summary tab in the roles violating segregation of duties view.
- Under the Security Roles grid, select the specific role to see the task separation violation.
- On this grid, you see the role name and total number of segregation of rules configured.
- After selecting a specific role, the data is loaded on the Segregation of duties rules.
- Go to the Segregation of duties rules grid.
- If multiple rules are configured for the selected role, there are multiple lines.
- Select the name of a specific rule to view the violation.
- The view shows the specific Segregation of duties rules that the selected role violates.
- Under the Infolog Text column, you will see all details of the violation.
View all violations
To view a report that lists all violations, go to System Administration > Security > Security Governance > Role violating segregation of duties > List.
The state uses the defined task allocation rules. All tasks are checked against these rules. If a task is assigned to a role that violates one of these rules, it appears in this report.

Leave a comment