The following reports are available to assist you with security, licensing, roles, and duties:
- User activity aging: This report follows sign-in information.
- License Summary: This report shows the number of entry points for each license level.
- Role audit trail: This report presents the history of an assigned and unassigned role to users.
- Security Analysis: This report provides information on the separate roles and their levels of access to privileges. It displays the number of users belonging to each role and the history of changes in responsibilities, roles, and privileges.
User activity aging report
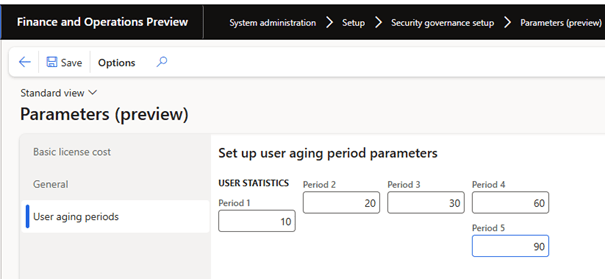
The User activity aging report tracks information related to connection to D365 finance. Therefore, it allows administrators to effectively monitor user activity. Some of the most common monitoring ranges are 10, 30, 60, 90 and 120 days. Daily ranges are configurable and can be customized to meet the needs of the organization. The data in this report is used to optimize license costs.
To define and customize day ranges for the Age Balance status of user activity, follow these steps.
1. Go to System Administration > setup > Security Governance Setup > Parameters.
2. In the User aging periods tab, configure all five-day ranges as required.
3. Select Save.
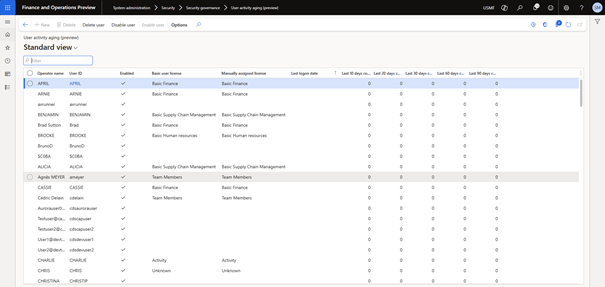
To see the results go to System Administration > Security > Security > Security Governance > User Activity Aging
License Summary report
The License Summary report helps users understand how many entry points for each license level are applied to users, roles, duties, and privileges. This information can be used to identify optimization opportunities in the organization.
- Recalculate prices – Recalculate the prices of licenses used for users, roles, duties, and privileges.
- Rebuild licenses – Rebuild the licenses used for users, roles, duties, and privileges. All users who have a small number of entry points at the operational license level may see their access redesigned and be moved to the activity or team member level.
- User license: list of all users, with details on items such as licenses, operations, and activities. You can use this list to check each user’s access and check the license level.
- Role license: list of all roles, with details on items such as licenses, operations, and activities. You can use this list to check the access of each role and check the license level.
- Duty license: list of all duties, with details on items such as licenses, operations, and activities. You can use this list to check the access of each duty and check the license level.
- Privilege license: list of all privileges, with details on items such as licenses, operations, and activities. You can use this list to check the access of each privilege and check the license level.
- User license summary: analyze user licenses and verify the details needed to assign licenses and optimize them for usability.
- Security summary: analyze user licenses, roles, duties, and privileges to optimize the environment and ensure that each user or group of users has appropriate access.

The license usage summary page displays different views of required licenses, such as users, roles and privileges. As with the security analysis form, the information must first be compiled using the Rebuild option.
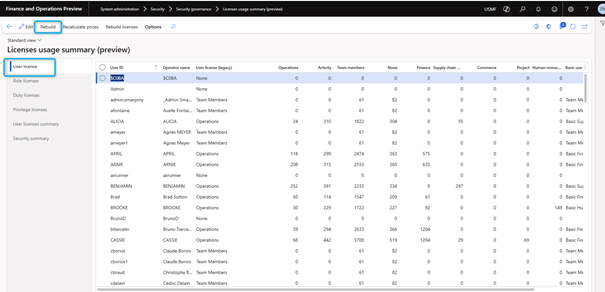
Instead of running a report, you will now have information about required licenses and a number of entry points related to a license level in a direct overview. You can then review whether it would be helpful to remove or change permissions to reduce licensing requirements for your organization.
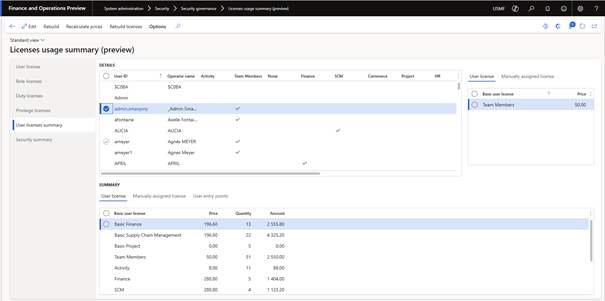
On the user license summary tab page, you can check the licenses required per person and a summary. Note that this is always an indication, and you will need to check the details, as this overview does not take into account any premium licenses. In addition, the view does not take into account the actual user licenses in Microsoft 365.
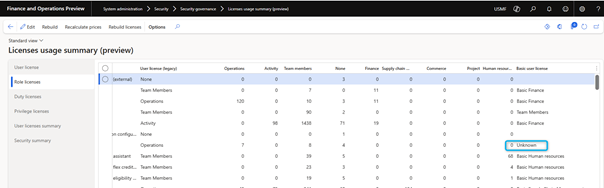
User security governance also involves an unknown license concept. The license level is based on both menu items and privileges used in a security role. In an internal table, there is a list of almost all privileges with a linked license SKU. For some duty and privilege, he knows nothing about license SKUs. As a fallback, it uses information from individual menu items where legacy license requirements are set on properties for a Maintain and View user license. To get the best recommendations on this form, I suggest using standard duties and privileges as much as possible when creating security roles.
Role audit trail report
The Role Audit Trail report shows a history of roles assigned and removed to users. Details include the time when a role was assigned and who assigned it. Data is collected from role assignments and deallocation of roles.
To view the Role audit trail status, follow one of these steps:
- Go to System administration > Users > User role.
- Go to System Administration >Security > Security Governance >Temporary Role Management.

Security analysis report
The Security Analysis report provides information about separate roles and their privilege levels. This information includes the number of users belonging to each role and a history of changes in duties, roles, and privileges. To update the status data, select Rebuild.
Users can identify security features by name. Permissions are displayed by level (Read, Create, Fix, Update, Invoke and Delete). The roles and their mappings to user licenses are displayed.
- Entry points: list of all system roles, sub-roles, duties, and privileges. Users can view all roles, duties, and privileges in one place.
- User entry points: get a complete security profile of a selected user. This profile shows which roles are assigned to the user, what duties and privileges are assigned to the roles, and which entry points are accessible to the user. Users can view other company users who have a similar level of access.
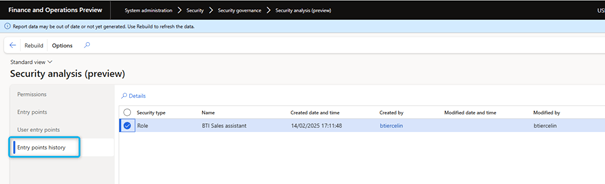
- Entry point history: get a complete history of changes to the security configuration. Various data points such as Creation date and time and Creation by are captured for roles, duties, and privileges. Users can also view the XML file and differences from the previous version of the same object.
In the security analysis form, you can view the relationships between the security objects and optionally start an export from a grid result to Excel. The screen may be completely blank at first. It is necessary to use the Rebuild option to create statistical tables resulting in different views on this form.
The User Entry Points tab page contains especially useful scanning information with a number of users and a list of associated users for security roles, duties, and all privileges. This can help answer audit questions, such as users with access to bank accounts of modified vendors.
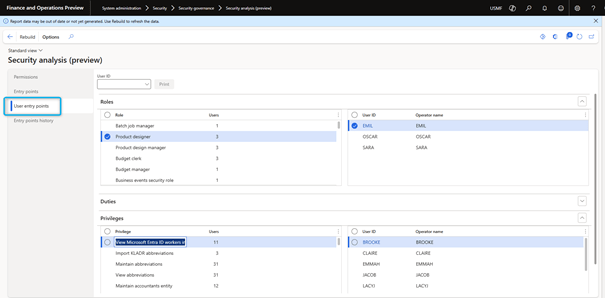
It is crucial to follow good naming conventions and reuse standard duties and privileges as much as possible.
The Entry Point History tab displays a log of all changes made to the Entry Points configured via the new User Security Governance features.

Leave a comment