Microsoft has introduced the concept of “AI agents” for some time. We now hear about “standalone ERP”. These two definitions are closely related. But what are AI agents? And what does ‘autonomous ERP’ mean?
In this article, I describe the link between ERPs, AI ERPs and autonomous ERPs. I also explain why AI agents are the cornerstones of autonomous ERP.
D365 Finance : Traditional ERP
D365 Finance is an ERP application. It is an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system that helps organizations automate and manage their key business processes for optimal performance. ERP software coordinates data flows between a company’s business processes, providing a single source of data and streamlining enterprise-wide operations. It is capable of linking the financial activities, supply chain, operations, commerce, reporting, production and human resources of a company on a single platform.
Looking at the module structure in D365 Finance, you can see this integration of business processes into various modules supporting processes in finance, supply chain, production, projects and more:
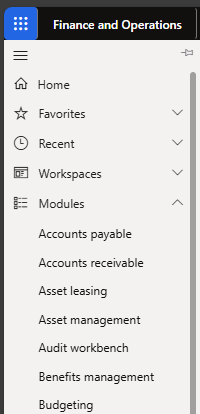
D365 Finance being an integrated solution, a single source of reliable data is accessible. For example, for stocks, quantities and values are available in a single database, where Purchasing, Inventories, Sales and Finance can view the same transactions to get an overview of their stocks:

The Heart of D365 Finance integrates various business processes into a centralized system that provides an overview of the organization’s operations. However, it often requires significant human interventions and manual data entry, which are time-consuming and error-prone.
D365 Finance becomes an “AI ERP”
With the integration of AI in D365 Finance, we are entering a new era. What does that mean? It is the ability of a computer system to mimic human cognitive functions, such as learning and problem-solving. Through mathematics and logic, a computer system simulates the reasoning used by humans to assimilate new information and make decisions.
AI systems make predictions or take measurements from existing data and can learn to gain in accuracy. Microsoft has already added standard features to D365 Finance. It can be features based on your licenses or features based on additional Copilot licenses, also offering new features compared to D365 Finance, such as Microsoft Copilot for Finance.
Microsoft calls its AI solutions “Copilot”. In D365 Finance, the features of Copilot are already available in several places:
- Contextual summaries by Copilot: AI-generated summaries with information about specific data such as suppliers, customers, orders or workflow history.

- The Copilot sidebar: a bot chat to help users use D365 Finance to consider when using it.
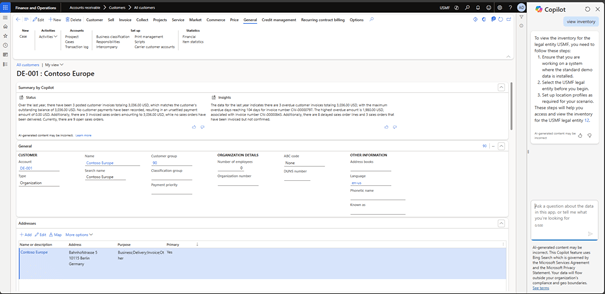
The introduction of AI in D365 Finance marked a significant advancement towards AI ERP. At this point, most AI options are designed to assist the user in working with D365 Finance. If Copilot is there to assist the user, he continues to perform the actions in the ERP.
D365 Finance will be a standalone ERP
The next step in this evolution is autonomous ERP, where AI not only intervenes as an assistant, but also as a proactive actor in D365 Finance to optimize business processes. The autonomous ERP is designed to be proactive, predictive and automate previously manual tasks.
That’s where the term ‘AI agents’ comes in. These agents are AI tools capable of managing tasks autonomously thanks to Microsoft Copilot. They can communicate actions to users or even act autonomously if allowed.
Standard agents will soon be available in D365 Finance, such as:
- The supplier communication agent: this agent autonomously manages collaboration with suppliers to manage procurement tasks: autonomously manages collaboration with suppliers to manage procurement tasks.
- The account reconciliation agent: this agent automates the reconciliation and clearing of transactions between sub-ledgers and the general ledger, helping finance teams provide better cash flow visibility and streamline the financial close process:
AI agents are created to perform specific tasks, in the above examples related to D365 Finance tasks for finance or supply chain management. Copilot is the personal AI assistant that assists you in your daily work. AI agents are created to handle specific tasks autonomously.
This means that each AI agent has a specific scope of action. Think of reconciliation agents, agents capable of automatically tracking emails from customers or suppliers in D365 Finance, or agents capable of creating reports and alerts from posts made in D365 Finance.
Power Automate and Copilot Studio also allow to create AI agents specific to each client to manage tasks in D365 Finance autonomously. Of course, human intervention is possible if necessary.
AI has allowed us to enter a new phase with ERPs like D365 Finance. AI may not be working perfectly yet and its impact on ERPs may still be limited. But I think it’s only a matter of time. AI is transforming the way we work with D365 Finance. But the success of AI agents also depends on 2 conditions that seem essential to me:
1 – The importance of well-organized processes when using AI agents
The benefits of an ERP like D365 Finance depend on the quality of processes within organizations. However, with the multiplication of human interventions, most organizations agree to execute their processes inefficiently at the global chain level. Automating additional tasks in D365 Finance through AI is, in my opinion, optimal in organizations where processes are well-defined, streamlined. The more we automate, the more important it becomes to have well-organized processes.
2 – Good data quality is crucial
Data quality is one of the main factors influencing the degree of automation of an ERP like D365 Finance. AI agents rely on the data they receive, for example because they are prompted by changes in data or use it to determine necessary follow-up actions. As a result, quality data is essential for relevant recommendations, analyses, predictions and actions in D365 Finance. If you wish to improve the quality of your data, check the following characteristics to evaluate them and define improvement actions:
- Reliable: Data should be based on reliable sources.
- Exact: the data must be correct and free of errors.
- Coherent: the data must be consistent within the overall chain of the company and the applications used by the company.
- Completeness: all necessary data must be available.
- Updated: the data must be up to date and available on time.
- Relevant: the data must be relevant in the context of business processes and associated decision-making.
- Unambiguously: all employees have the same interpretation of the data, regardless of their role and experience in the organization.

Leave a comment